
TCAD Modeling of Amorphous Selenium-based Avalanche Photon Detectors
Abstract— Silvaco TCAD simulations are employed to identify relevant current carrying mechanisms in amorphous selenium (a-Se) based detectors, using parameters obtained from experimental data, density functional theory calculations, and in-house bulk Monte Carlo simulations. The steady-state dark current behaviors in various a-Se detectors are analyzed by identifying all relevant current conduction mechanisms (e.g., space-charge limited current, bulk thermal generation, Schottky emission, Poole-Frenkel activated mobility and hopping conduction), as well as “acceptor” and “donor” defect density of states located in the forbidden band gap of a-Se. The theoretical models are validated by comparing them with experimental steady-state dark current densities in avalanche and non-avalanche a-Se detectors.

Singular Point Source MOS Cell Concept (S-MOS) Implemented on a Narrow Mesa Trench IGBT
Abstract— A Singular Point Source MOS (S-MOS) cell concept suitable for power MOS based devices is presented. The S-MOS differs from a standard Planar or Trench MOS cell in the manner by which the total channel width per device area is devised. The S-MOS single cell channel width is defined as the peripheral length of a line running approximately along the N++ source and P channel junction which is positioned on a gated trench side-wall. The length of the line is established from a singular point implant source for forming the N++ source region which geometrically corresponds to the shape of the N++/P junction. The N++ and PChannel profiles achieved are similar to those for a planar cell, but for the S-MOS, they are situated on a trench side-wall. The total device channel width will therefore depend on the total number of gated trench side-walls per chip. The S-MOS provides a unique approach for MOS cell layout designs and is applicable to different MOS based power devices. In this paper, the S-MOS is implemented on a 1200V IGBT by means of 3D-TCAD simulations while providing results highlighting the potential advantages with respect to the device static and dynamic performance.
Keywords – MOS cell, Insulated gate bipolar transistors.
A Comprehensive Oxide-Based ReRAM TCAD Model with Experimental Verification
Abstract—During the last few years, oxide-based ReRAM technology has attracted intense industrial and scientific research interest. Therefore, we have performed an in-depth computational study with a focus on data retention besides the resistive switching and the current run-away. Our newly developed comprehensive TCAD (Technology Computer Aided Design) model provides deep insight into the underlying microscopic processes and is validated against experimental data as an accurate and predictive simulation tool.

2021 TCAD Baseline Release
New Features in 2021 Baseline Release:
- Section 1: Process Simulation
- Section 2: Device Simulation
- Section 3: Victory Mesh
- Section 4: Parasitic Extraction

An Introduction to Meshing in Victory Process
Victory Process (VP) uses two types of mesh to represent the structure:
• The geometry mesh, which is used to represent the material regions.
• The volume mesh, which is used to represent the volume data (doping etc).
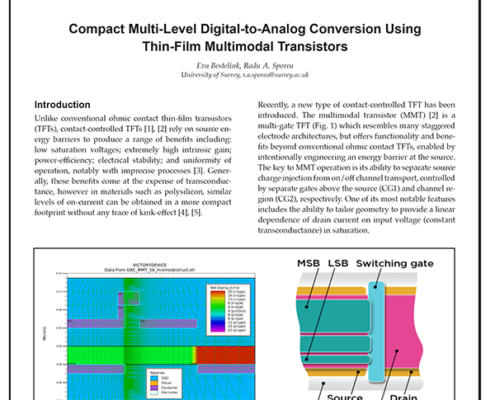
Compact Multi-Level Digital-to-Analog Conversion Using Thin-Film Multimodal Transistors
Unlike conventional ohmic contact thin-film transistors (TFTs), contact-controlled TFTs [1], [2] rely on source energy barriers to produce a range of benefits including: low saturation voltages; extremely high intrinsic gain; power-efficiency; electrical stability; and uniformity of operation, notably with imprecise processes [3]. Generally, these benefits come at the expense of transconductance, however in materials such as polysilicon, similar levels of on-current can be obtained in a more compact footprint without any trace of kink-effect [4], [5].

Investigation and Explanation of PiPiN Avalanche Photo-Diode Characteristics
In this article, the operation of avalanche photo-diodes in the medium gain, continuous operation mode is investigated. In other words, we are not considering diode operation in transient “Gieger” or “single photon” detection mode, but rather in a region safely below secondary breakdown, where a well-designed avalanche photo diode can exhibit a moderate photo-generated current multiplication factor of an order of magnitude or higher.
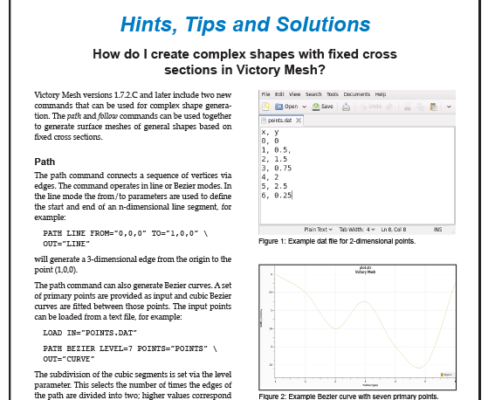
How do I create complex shapes with fixed cross sections in Victory Mesh?
Victory Mesh versions 1.7.2.C and later include two new commands that can be used for complex shape genera-tion. The path and follow commands can be used together to generate surface meshes of general shapes based on fixed cross sections.PathThe path command connects a sequence of vertices via edges. The command operates in line or Bezier modes. In the line mode the from/to parameters are used to define the start and end of an n-dimensional line segment, for example:

Parabolic Grading of a PHEMT Channel Composition for Ultra-High and Broad OIP3 Peak
We detect a local maximum in the design space of a pseudomorphic-channel high electron mobility transistor (PHEMT). The design has an OIP3 linearity figure-of-merit that is 10-15 dBm above the baseline for a similar 1 mm width control device, and is achieved at a gate bias on the order of 100 mA/mm or less, where the ratio of transconductance to the bias current gm1/ID is particularly large (7 volt-1).
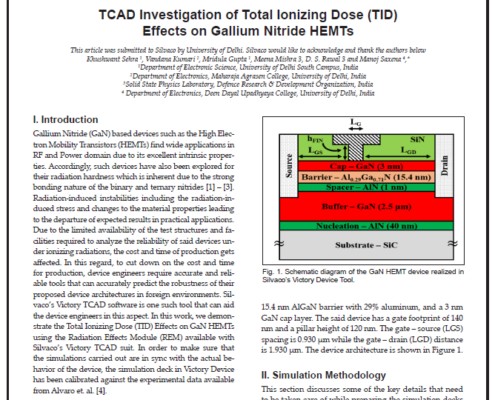
TCAD Investigation of Total Ionizing Dose (TID) Effects on Gallium Nitride HEMTs
Gallium Nitride (GaN) based devices such as the High Electron Mobility Transistors (HEMTs) find wide applications in RF and Power domain due to its excellent intrinsic properties. Accordingly, such devices have also been explored for their radiation hardness which is inherent due to the strong bonding nature of the binary and ternary nitrides. Radiation-induced instabilities including the radiation-induced stress and changes to the material properties leading to the departure of expected results in practical applications. Due to the limited availability of the test structures and facilities required to analyze the reliability of said devices under ionizing radiations, the cost and time of production gets affected. In this regard, to cut down on the cost and time for production, device engineers require accurate and reliable tools that can accurately predict the robustness of their proposed device architectures in foreign environments. Silvaco’s Victory TCAD software is one such tool that can aid the device engineers in this aspect. In this work, we demonstrate the Total Ionizing Dose (TID) Effects on GaN HEMTs using the Radiation Effects Module (REM) available with Silvaco’s Victory TCAD suite.
