
Simulation of a DBR Edge Emitting Laser with External Air Gap Tuning Mirror
A methodology for simulating an edge emitting laser is demonstrated that incorporates a distributed Bragg Reflector (DBR) as one of the mirrors, with the other being a variable air gap external planar mirror that is used as a method for fine tuning the lasing wavelength. This type of calculation requires non uniformity of the dielectric’s static and dynamic (pumping) properties in both the transverse and longitudinal directions, together with self consistent coupling to the external tuning cavity. A key challenge addressed is the proper treatment of the open nature of the cavity, such that the amplitudes of the outgoing waves leaving the facets are consistent with the cavity interior and facet reflectivity. Mode competition and hopping are natural consequences of the methodology developed. In the model developed here, the spatial hole burning effects, cross and self-saturation effects can be included while accounting for the degree of spatial overlap of modes. We also account for diffraction losses at the output facet which can become important in the case of strong index guiding.

Anode Shorts Layout Dependence of Bi-mode IGBT (BiGT) On-state Characteristics
A new class of high-voltage semiconductor devices, known as a reverse conducting IGBT (RC-IGBT), has emerged in recent years from research efforts to diminish the usage of external anti-parallel free-wheeling diode chips for IGBT switching applications. The RC-IGBT device concept is based on the monolithic integration of a freewheeling diode into an IGBT chip. Hereby, an anti-parallel diode is formed through the embedment of an n+ region in an anode/collector region of the IGBT. Both the n+ region and the p+ anode are then shorted together by an anode/collector contact. Although the RC-IGBT has many advantages over the conventional IGBT, especially in terms of manufacturing cost, total chip size and reliability of power modules, it is detrimental to the snapback effect at forward conduction of IGBT mode.
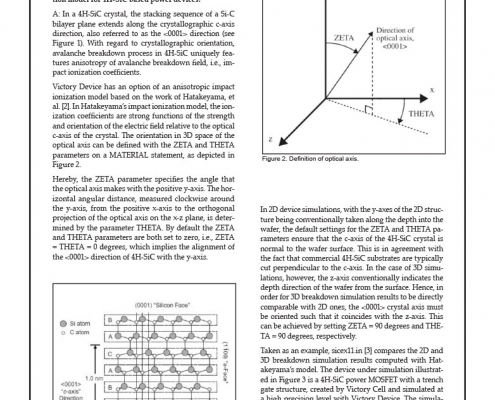
Hints, Tips and Solutions – Compare the Results of Breakdown Simulations with Hatakeyama’s Impact Ionization Model for 4H-SiC Based Power Devices
In a 4H-SiC crystal, the stacking sequence of a Si-C bilayer plane extends along the crystallographic c-axis direction, also referred to as the <0001> direction (see Figure 1). With regard to crystallographic orientation, avalanche breakdown process in 4H-SiC uniquely features anisotropy of avalanche breakdown field, i.e., impact ionization coefficients.

2D IBC-SHJ Solar Cell Simulation and Optimization
Interdigitated back contact silicon heterojunction (IBC-SHJ) combines the advantages of interdigitated back contact (IBC) and silicon heterojunction (SHJ) solar cells. Having all the contacts at the back of the cell eliminates contact shading, leading to a higher short-circuit current (JSC). Being a heterojunction device, IBC-SHJ also has the potential of higher open circuit voltage (VOC) due to the better surface passivation of the deposited amorphous silicon (a-Si) layer. The low temperature deposition, instead of high temperature diffusion, decreases thermal stress, which is the trend of future silicon solar cells. Rear surface passivation by deposited intrinsic amorphous silicon (a-Si) buffer layer in IBC-SHJ solar cells significantly improves open circuit voltage (VOC) and short circuit current (JSC) but can lead to very low fill factor (FF) with an “S” shape J-V curve. In this paper, methods to optimize IBC-SHJ solar cell with improved FF are discussed and guided by two-dimensional numerical simulation. The modeling of the IBC-SHJ solar cell requires device simulation software operating in two dimensions and incorporating amorphous silicon. To study this innovative structure, we use ATLAS two-dimensional (2-D) device simulation software that provides accurate bulk and interface defects needed to model amorphous silicon. We first present the geometrical structure of the solar cell, then review the general framework of the simulation by specifying the different physical models, and finally examine the simulation results in order to determine the important parameters to achieve high efficiency.

State of the Art 2D and 3D Process and Device Simulation of GaN-Based Devices
Silicon has long been the semiconductor of choice for high-voltage power electronics applications. However, wide-bandgap semiconductors such as SiC and GaN have begun to attract attention because they are projected to have much better performance than silicon. In comparison with silicon, wide-bandgap semiconductors offer a lower intrinsic carrier concentration, a higher electric breakdown field, a higher thermal conductivity, and a faster saturated electron drift velocity.
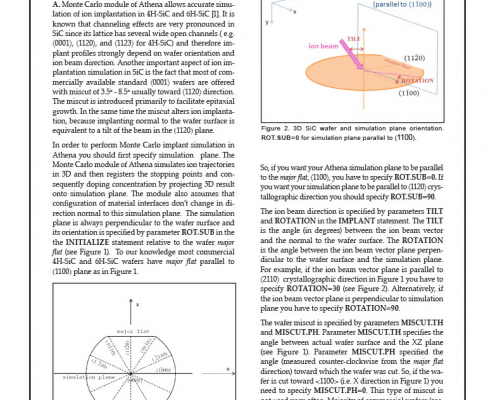
Hints, Tips and Solutions – Setup Athena Monte Carlo Simulation of Ion Implantation in Silicon Carbide
Monte Carlo module of Athena allows accurate simulation of ion implantation in 4H-SiC and 6H-SiC [1]. It is known that channeling effects are very pronounced in SiC since its lattice has several wide open channels ( e.g. 〈0001〉, 〈1120〉, and 〈1123〉 for 4H-SiC) and therefore implant profiles strongly depend on wafer orientation and ion beam direction. Another important aspect of ion implantation simulation in SiC is the fact that most of commercially available standard 〈0001〉 wafers are offered with miscut of 3.5° - 8.5° usually toward 〈1120〉 direction. The miscut is introduced primarily to facilitate epitaxial growth. In the same time the miscut alters ion implantation, because implanting normal to the wafer surface is equivalent to a tilt of the beam in the (1120) plane.

TCAD Simulation of Multiple Quantum Well Infrared Photodetector (QWIP)
We demonstrate the capabilities of SILVACO TCAD tools for the design and simulation of intersubband GaAs/AlGaAs multiple quantum well infrared photodetectors. We compute the photoconductive gain spectrum of the device self consistently with the charge flow, non-radiative capture-escape, and intersubband transitions in the active region. The solid state calculations provide input to a light propagation modeling tool that allows for multiple reflections in the layered geometry of the active region. From this full calculation, we extract light absorption and quantum efficiency as a function of the angle of incidence and the wavelength of a mono-spectral beam of light. This TCAD simulation can be used as a starting point by design engineers for obtaining guide lines to analyze and optimize quantum well infrared photodetectors.
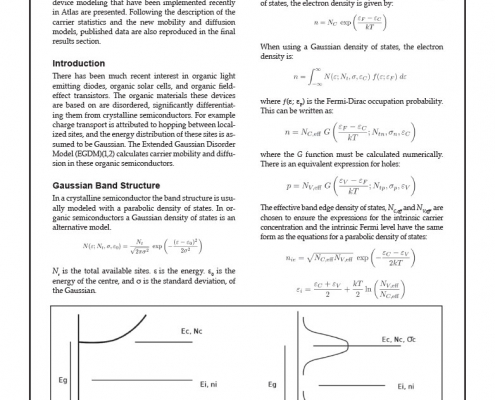
The Extended Gaussian Disorder Model in Atlas
In this article the various enhancements to the organic device modeling that have been implemented recently in Atlas are presented. Following the description of the carrier statistics and the new mobility and diffusion models, published data are also reproduced in the final results section.

Simulation of Ion Beam Etching of Patterned Nanometer-scale Magnetic Structures for High-Density Storage Applications
Fabrication of various nano-structures often requires mask controlled or patterned etching of materials. The chemical or wet etch methods cannot be used for nanoscale geometries due to the substantial isotropic component of etch rate. Therefore, various plasma or reactive ion etching method are typically used. Unfortunately, some materials do not easily form volatile reaction products and all types of chemically assist etching becomes problematic. Among those materials are elements such as Co, Ni, Fe, Pt, and Cr which are usually used in magnetic nano-structure technologies. Therefore, ion beam etching or ion milling is the most suitable method to pattern these materials [1].

State of the Art 3D SiC Process and Device Simulation
Silicon has long been the semiconductor of choice for high-voltage power electronics applications [1,2]. However, wide-bandgap semiconductors such as SiC have begun to attract attention because they are projected to have much better performance than silicon [3-7]. In comparison with silicon, wide-bandgap semiconductors offer a lower intrinsic carrier concentration (10 to 35 orders of magnitude), a higher electric breakdown field (4 to 20 times), a higher thermal conductivity (3 to 13 times), and a faster saturated electron drift velocity (2 to 2.5 times).
