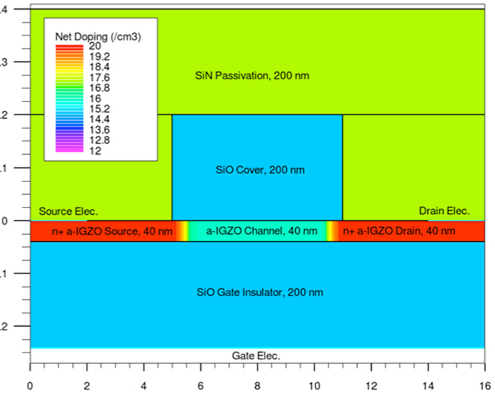
Channel-length Dependence of a-IGZO TFTs with Self-heating Effects
Introduction
Amorphous In-Ga-Zn-O thin-film transistors (a-IGZO TFTs) show a high mobility, a small sub-threshold swing, and a low OFF-current, and they are considered to be one of the most promising TFT for new flat-panel displays (FPDs). The high mobility originates from the unique electron transport in a-IGZO. The transport properties are different from those in conventional semiconductor materials like Si, for example, the mobility increases with increase of the electron concentration and/or temperature. Therefore, the new mobility model for a-IGZO is necessary. In addition, as pixel sizes in the FPDs decreases, a channel-length, L, of a-IGZO TFTs becomes shorter. It indicates that it is important to understand the operation of short-channel a-IGZO TFTs.
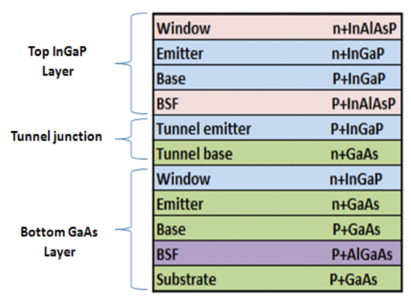
Simulation of Different Tunnel Junctions in InGaP/GaAs, InGaP/CdTe Dual Junction Solar Cells
Abstract — Dual junction solar cells were simulated using Silvaco TCAD tool with various tunnel junction material compositions. InGaP/GaAs dual junction solar cells were simulated with 10 different tunnel junction combinations. The highest efficiencies were from InGaP/AlGaAs and InGaP/InGaP tunnel junctions at 31.82% and 31.75%. InGaP/CdTe solar cells were also simulated with four different tunnel junction combinations. InGaP/InGaP tunnel junction was found to be most efficient with 37.29% which is consistent with experimental data. Three of four InGaP/CdTe dual junction solar cells were simulated to have higher efficiency values than all InGaP/GaAs solar cells.
Hints, Tips and Solutions – July, August, September 2019
Q. Is it possible to emulate a deep reactive ion etch process (e.g. deep trench with scalloped sidewalls) without using a physical based process simulation, such as Victory Process?
To study a non-ideal geometry and its impact on device performance, TCAD device engineers may want to generate structures with complex geometries quickly, without the added details of physically-based process simulation.
Process Simulation – New Features in 2019 Baseline Release
2019 baseline release of Victory Process includes improvements and extensions to the following modules:
Physical etching/deposition
Stress simulation
Annealing/oxidation
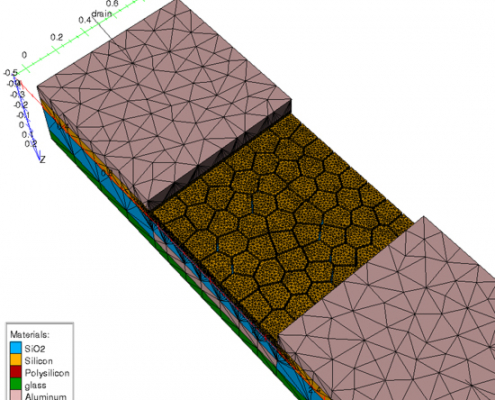
Meshing – New Features in 2019 Baseline Release
The 2019 TCAD baseline release of Victory Mesh now contains Solid Modeling functionality. The term Solid Modeling is used to refer to a methodology that generates or manipulates a device via geometrical operations, for example, bending, mirroring and joining or insertion.
Device Simulation – New Features in 2019 Baseline Release
The effect of Coulomb interaction in the absorption spectrum of quantum wells (QWs) is responsible for the quantum confined Stark effect (QCSE), which is the physical mechanism underlying the operation of electro-absorption modulators [1].
A new model has been added to Atlas to simulate QCSE in QWs and can be enabled with the following command (the qwell model must also be activated):
Interactive Tools – New Features in 2019 Baseline Release
DeckBuild is Silvaco’s state of the art simulator interface. It is capable of running all simulators from Silvaco as well as many of the visualization tools. Figure 4-1 shows an overview where a simulation was successfully finished and the results can be inspected. Values that were extracted from a structure file are shown in the top right part of the window.
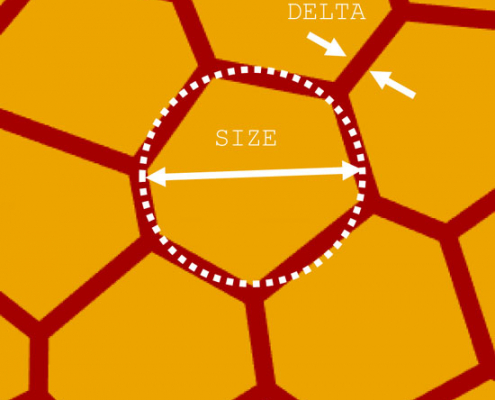
3D TFT Simulation of Grains and Grain Boundaries
Introduction
Low-temperature polycrystalline silicon (LTPS) thin-film transistors have been widely applied to AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode) as the most suitable means for high mobility, high switching speed and high resolution [1-2].
A Laser Annealing Process such as Excimer Laser Annealing (ELA) is used to manufacture by converting Amorphous Silicon (a-Si) to Polycrystalline Silicon (poly-Si) at low temperature. The poly-Si structure (produced through ELA) shows the laser wavelength, pulse width and spatial beam dependencies.
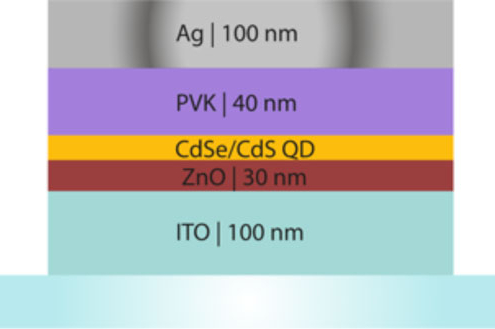
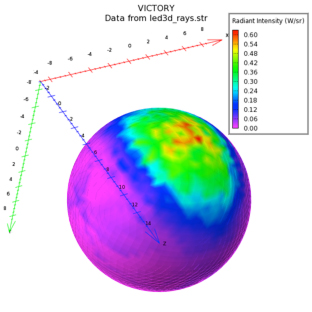
Quantum Dot-Based Hybrid Light Emitting Diode Modelling Using Radiant
Introduction
With the recently launched Radiant, a graphical user interface (GUI) for Atlas-based TCAD simulations, the entry barrier for inexperienced users has been lowered. In particular, the use of guided simulation tools, for both experienced and novice researchers, can speed up the development cycle. Light emitting diodes (LEDs) have caught the attention of the scientific community for many years, especially organic-based light emitting diodes (OLEDs) and the emerging quantum dot-based light emitting diodes (QD-LEDs).
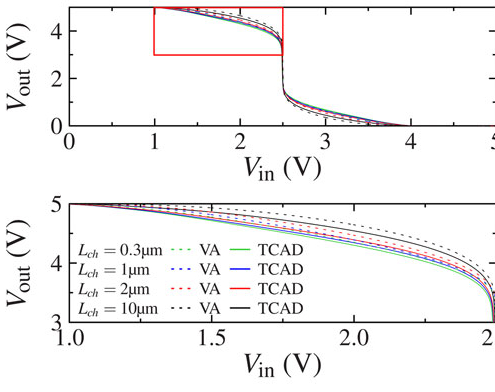
Verification of an Compact Model for Organic Thin-Film-Transistors by Using MixedMode Creating an CMOS Inverter Circuit with TCAD Transistor Devices
Organic thin-film transistors (OTFTs) are promising devices for future low-cost electronics[1][2]. However, to enable the development of this technology, circuit design simulation is needed. TCAD with MixedMode approach provides a suitable route for the physics based simulation of these transistors within simple circuits. As circuits become more complicated, more devices are needed and the computing time increases significantly. Compact models describe the behavior of the device with only a few equations and thus the computing time is reduced to a viable magnitude. Such equations are written down in a Verilog-A format which can be used by most SPICE simulators.
