
How to Achieve Good Parameter Optimization Using The New Methodology in UTMOST III Optimizer
Optimization is the task of finding the absolute best set of admissible conditions to achieve your objective, formulated in mathematical terms. The goal of optimization is, given a system, to find the setting of it's parameters so that to obtain the optimal performance. The performance of the system is given by an evaluation function. Optimization problems are commonly found in a wide range of fields, and it is also of central concern to many problems.
How to extract BSIM4 parameters using UTMOST III
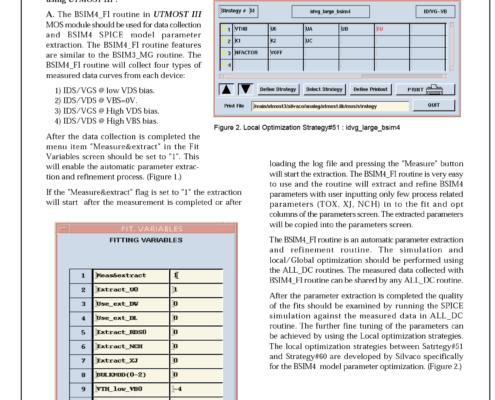
The BSIM4_FI routine in UTMOST III MOS module should be used for data collection and BSIM4 SPICE model parameter extraction. The BSIM4_FI routine features are similar to the BSIM3_MG routine. The BSIM4_FI routine will collect four types of measured data curves from each device.

Connectivity Options for DRC Spacing Check Operations in Savage
An IC layout has to satisfy many technological design requirements. One of these is spacing, i.e., a layout object has to be separated from another one by some minimal distance. In addition, any spacing requirement (e.g. minimal distance between layout objects) varies depending on the particular features of the layout objects, e.g. the layer the objects belong to, the purpose of these objects, etc.

Recent improvements in Expert, Savage, Guardian and Maverick
Most of recent improvements in Expert, Savage, Guardian and Maverick are aimed at the enhancement of the usability of these tools. All features described are developed according to the requests of our customers.

Optimal Packing of Orthoblocks For ULSI Floorplanning
Virtually all latest and prospective enhancements of Expert Layout processor (for example, semi-automatic floorplanning) are based on sophisticated geometrical models. In some cases some advanced mathematical research is necessary to develop efficient algorithms. This article is devoted to the problem of optimal packing of orthoblock which is originated from several areas of VLSI design automation.

Hints, Tips and Solutions for Expert Layout Editor
If I try to close a project, Expert gives me a prompt: "Save changes in a project?", but I remember that I didn't do any editing of cells. When can be the reason. The second question is: how do I know which cells were modified?

Simulating Impurity Freeze-Out During Low Temperature Operation
The low temperature operation of many device structures has been shown as an effective method for improving device performance without reducing device size. By modeling low temperature phenomena, numerical simulation of device operation at low temperatures provides an effective means for analyzing such performance improvements before investing manufacturing time or money. It is the purpose of this paper to discuss the modeling of the dopant freeze-out phenomenon in ATLAS and provide an application example of its use.

Simulation of Vertical Double-Gate SOI MOSFETs Using Device3D
This article will present the simulation methodology of a self-aligned double-gate MOSFET structure (FinFET) using SILVACO 3-D simulation suite. The double-gate MOSFET is one of the most attractive alternative to classical MOSFET structure for gate length down to 20nm. The main advantage of the FinFET is the ability to drastically reduce the short channel effect. In spite of his double-gate structure, the FinFET is closed to its root, the conventional MOSFET in layout and fabrication. 3-D numerical simulations of the FinFET are performed in this article, in order to validate the basic principles and to uncover several important aspects: evaluation of the length , width and quantum effects.

Non-Stationary Transport Effects: Impact on Performances of Realistic 50nm MOSFET Technology
We analyze quantitatively the real impact of technology on the needed level for carrier transport modeling. The results, based on theoretical analyzes, are applied to existing devices. This work shows which recipes must be used to evaluate the performances of advanced device architectures (down to 50nm gate length). An original point of this work is the investigation of technology influence (channel doping and LDD doping) on injection velocity at source side and on drain current. The results open the perspective of specific engineering of access regions in order to take full advantage of non-stationary effects on the drain current.

ATLAS can be used to perform large signal sinusoidal analysis
The Atlas syntax is flexible enough to allow the definition of sinusoidal nodal voltages by defining them on the SOLVE statement line. To illustrate this the structure shown in Figure 1 has been used. Before the sinusoidal pulse is applied a dc operating condition is set with
