Simulation Standard
Technical Journal
A Journal for Process and Device Engineers
Hints, Tips and Solutions – Types of 3D Delaunay Shape Refinement
Q: What Types of 3D Delaunay Shape Refinement can be used in Victory Process?
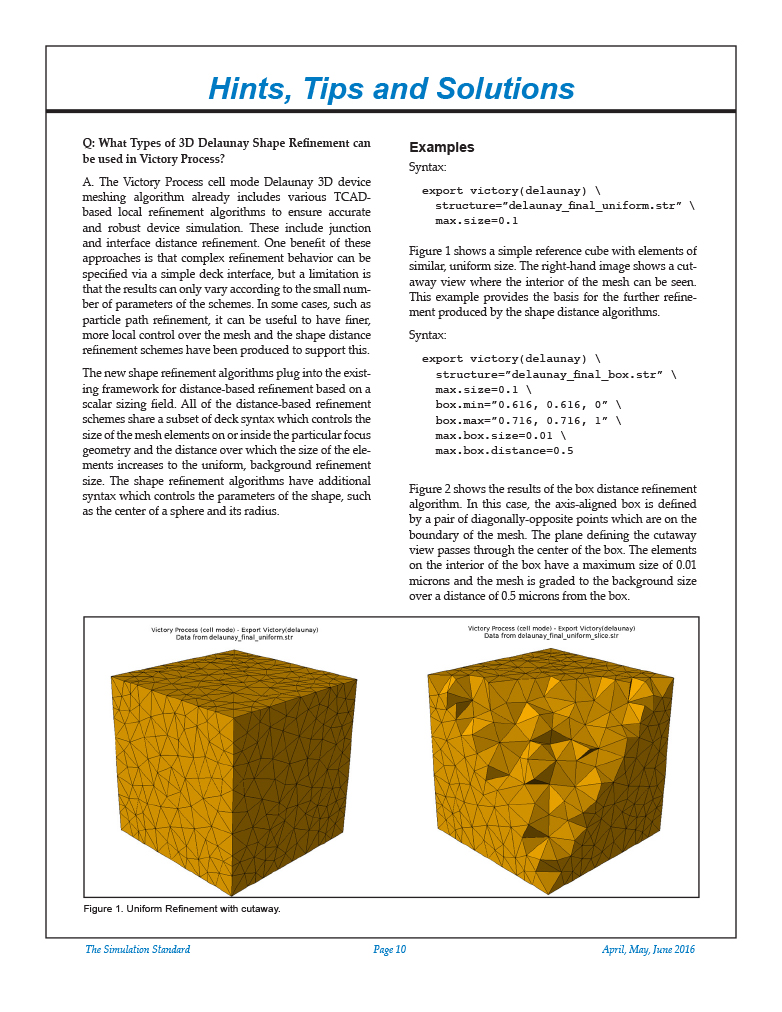
A. The Victory Process cell mode Delaunay 3D device meshing algorithm already includes various TCAD-based local refinement algorithms to ensure accurate and robust device simulation. These include junction and interface distance refinement. One benefit of these approaches is that complex refinement behavior can be specified via a simple deck interface, but a limitation is that the results can only vary according to the small number of parameters of the schemes. In some cases, such as particle path refinement, it can be useful to have finer, more local control over the mesh and the shape distance refinement schemes have been produced to support this.
Blue LED Simulation
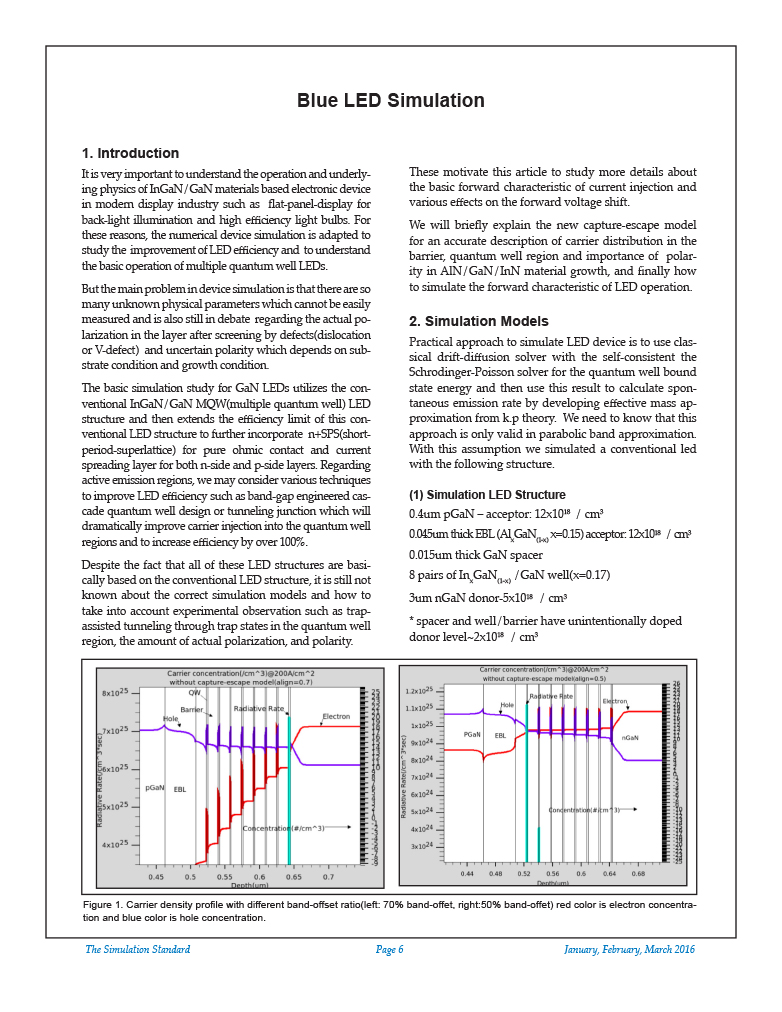
It is very important to understand the operation and underlying physics of InGaN/GaN materials based electronic device in modern display industry such as flat-panel-display for back-light illumination and high efficiency light bulbs. For these reasons, the numerical device simulation is adapted to study the improvement of LED efficiency and to understand the basic operation of multiple quantum well LEDs.

Unified Victory Conformal Export for 2D Process Mode
Victory Process can operate in either 1, 2 or 3-dimensions and can produce one of two different geometric representations: cell mode and process mode. Cell mode structures are generally composed of large, flat geometric parts but process mode structures may be smoothly varying and only very locally flat. Device meshes of cell mode structures resolve the input shape precisely but this is undesirable for the case of process mode structures as it would result in very finely sampled meshes which would be unsuitable for device simulation.

a-IGZO TFT Simulation
The flat panel device for active matrix liquid crystal displays (AMLCDs) and active matrix organic light-emitting diode displays (AMOLEDs) has utilized a low cost amorphous silicon or low temperature poly-silicon (LTPS) as a fast switching transistor in mobile devices,TVs, and other display consumer electronics. Recently, amorphous InGaZnO (a-IGZO) thin-film transistor (TFT) is now one of the most important materials in the display area for flexibility, large-area uniformity and high mobility. The conventional a-Si:H TFT or LTPS devices have many degradation problems such as bias stress and photo induced instabilities that are the most important factors which must be fully understood and analyzed to improve the device design. These instabilities come from time-dependent density of states (DOS) change in forbidden band gap of material during device operation.

Hints, Tips and Solutions – Crop and Slice using a non-convex mask in Victory Process export
Q. How can I Crop and Slice using a non-convex mask during the export?
Non-Convex Mask Polygons
Non-Convex Mask Polygons
Previous Victory Process releases have supported convex polygon cropping, slicing and mirroring support. It is also now possible to use non-convex polygons for either cropping or slicing.
In Figure 1 an example of a non-convex polygon crop and slice in the cell mode victory (delaunay) export is given. Note that the deck syntax is identical to the convex case.
2D Crop, Slice and Mirror
It is possible to perform the crop, slice and mirror (process and/or device) in the 2D exports.
An example of this functionality is given in Figure 3, where a crop and slice is shown. It should be noted that the coordinates specified in the polygon mask are those in the 2D export and not the 3D grid that the export is taken from (i.e., only X/Y need to be specified even though this cutplane is XZ).
Performance Evaluation of a New Hybrid MPI-thread Parallelized Direct Solver
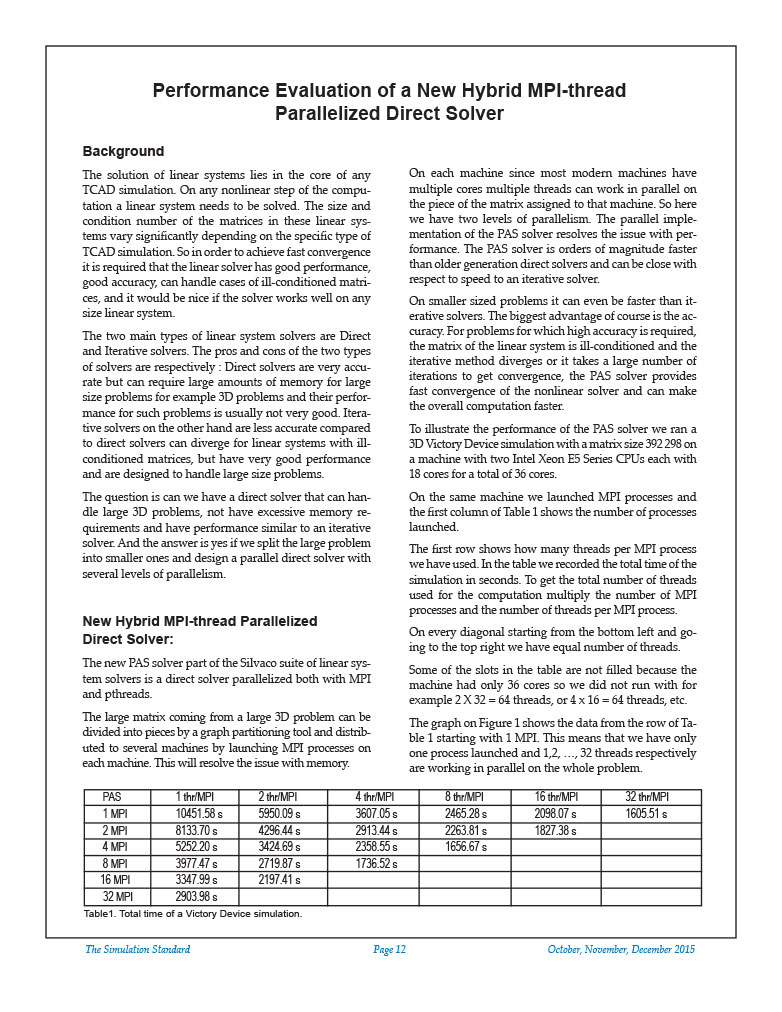
The solution of linear systems lies in the core of any TCAD simulation. On any nonlinear step of the computation a linear system needs to be solved. The size and condition number of the matrices in these linear systems vary significantly depending on the specific type of TCAD simulation. So in order to achieve fast convergence it is required that the linear solver has good performance, good accuracy, can handle cases of ill-conditioned matrices, and it would be nice if the solver works well on any size linear system.

