New Feature of Quantum Module: Schrödinger-Poisson Solver for Nanowire Application
Introduction
The trend toward ultra-short gate length MOSFET requires a more and more effective control of the channel by the gate leading to new architecture like double-gate, tri-gate, omega-gate, and four-gate (or gate-all-around) MOSFETs. Recent advances in nanoscale fabrication techniques have shown that semiconductor nanowires are becoming promising candidates for next generation technologies. In particular, silicon nanowire transistors have been demonstrated by several research groups with cross-sectional dimensions in the range of several nanometers.
To address a strong quantum confinement effect in a nanowire cross-section, SILVACO has recently enhanced its Quantum Module [1]. Along with a general 2D Schrödinger solver valid for any cross-sectional shape, a new solver was developed to specifically account for the natural cylindrical symmetry of the nanowire. This article presents these new features.
Nanowire: Geometry and Structure
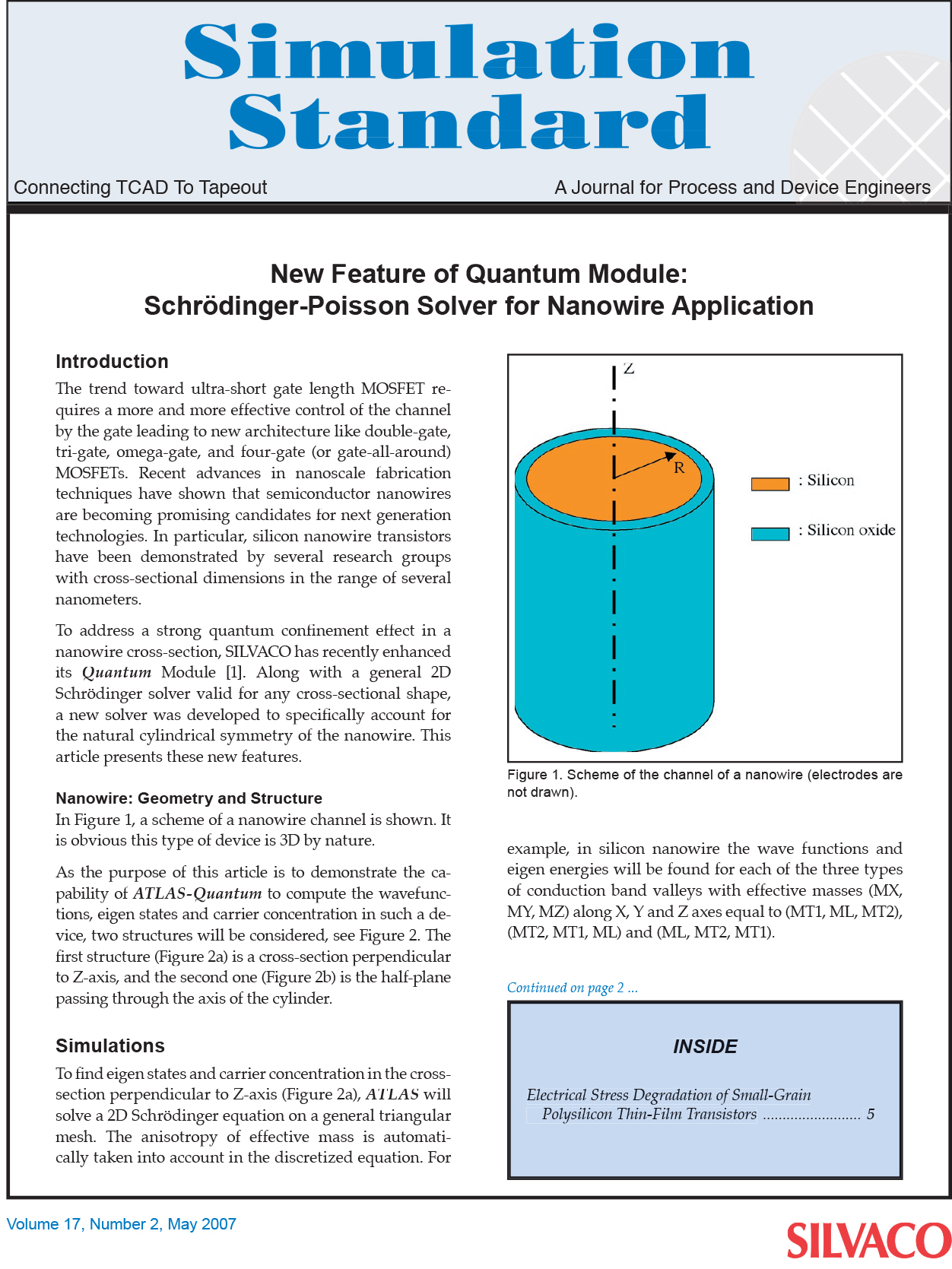
In Figure 1, a scheme of a nanowire channel is shown. It is obvious this type of device is 3D by nature.