Simulation Standard
Silvaco面向半导体工艺和器件仿真工程师推出的技术刊物

A Novel Approach to Three-Dimensional Semiconductor Process Simulation: Application to Thermal Oxidation
Abstract
The paper presents a new approach to three-dimensional semiconductor process simulation that overcomes the problem of moving boundaries and mesh generation. Contrary to using unstructured meshes, the approach makes use of the level set method on fixed Cartesian meshes. A concept of multi-layer structure is introduced to capture an arbitrary complex structure. To handle a big geometrical scale ratio in a structure, the concept of adaptive mesh refinement is used. A special in-house finite-difference scheme is designed to approximate the relevant equations near material interfaces. In the bulk of regular nodes the standard finite difference schemes are used. Application of the approach to the modeling of oxidation of some typical types of structures used in semiconductor technology is demonstrated.
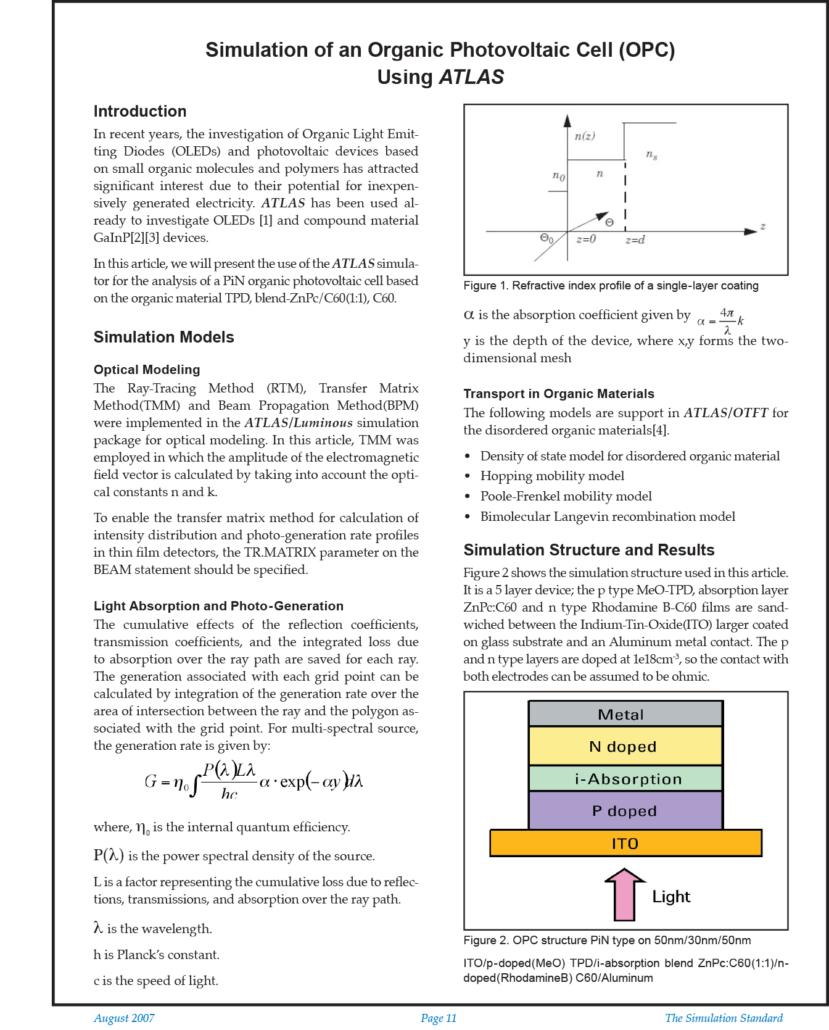
Simulation of an Organic Photovoltaic Cell (OPC) Using Atlas
Introduction
In recent years, the investigation of Organic Light Emitting Diodes (OLEDs) and photovoltaic devices based on small organic molecules and polymers has attracted significant interest due to their potential for inexpensively generated electricity. ATLAS has been used already to investigate OLEDs [1] and compound material GaInP[2][3] devices.
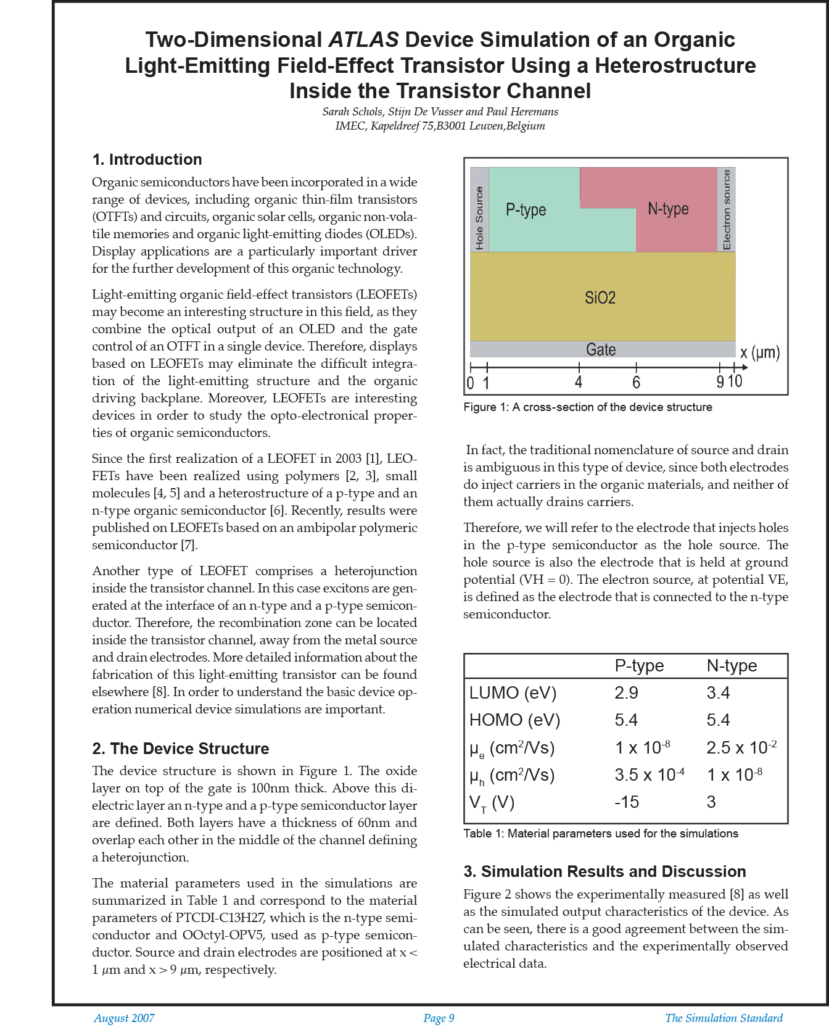
Two-Dimensional Atlas Device Simulation of an Organic Light-Emitting Field-Effect Transistor Using a Heterostructure Inside the Transistor Channel
1. Introduction
Organic semiconductors have been incorporated in a wide range of devices, including organic thin-film transistors (OTFTs) and circuits, organic solar cells, organic non-volatile memories and organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs). Display applications are a particularly important driver for the further development of this organic technology.

Electrical Stress Degradation of Small-Grain Polysilicon Thin-Film Transistors
Abstract
This paper is focused on the stability of n-channel laser-crystallized polysilicon thin-film transistors (TFTs) submitted to a hydrogenation process during the fabrication and with small grains dimension. With the aid of numerical simulations, we investigate the effects of static stress using two types of procedures: the on stress and the hot carrier stress. Results show that the variations of trap state density into the whole polysilicon layer and not only near the drain junction are responsible for the degradation of TFTs performances in both the two types of stress and that the interface trap states play a negligible role compared to the bulk trap states.

Trapping Effects in the Transient Response of AlGaN/GaN HEMT Devices
In this paper, the transient analysis of an AlGaN/GaN high-electron mobility transistor (HEMT) device is presented. Drain–current dispersion effects are investigated when gate or drain voltages are pulsed. Gate-lag and drain-lag turn-on measurements are analyzed, revealing clear mechanisms of current collapse and related dispersion effects. Numerical 2-D transient simulations considering surface traps effects in a physical HEMT model have also been carried out.
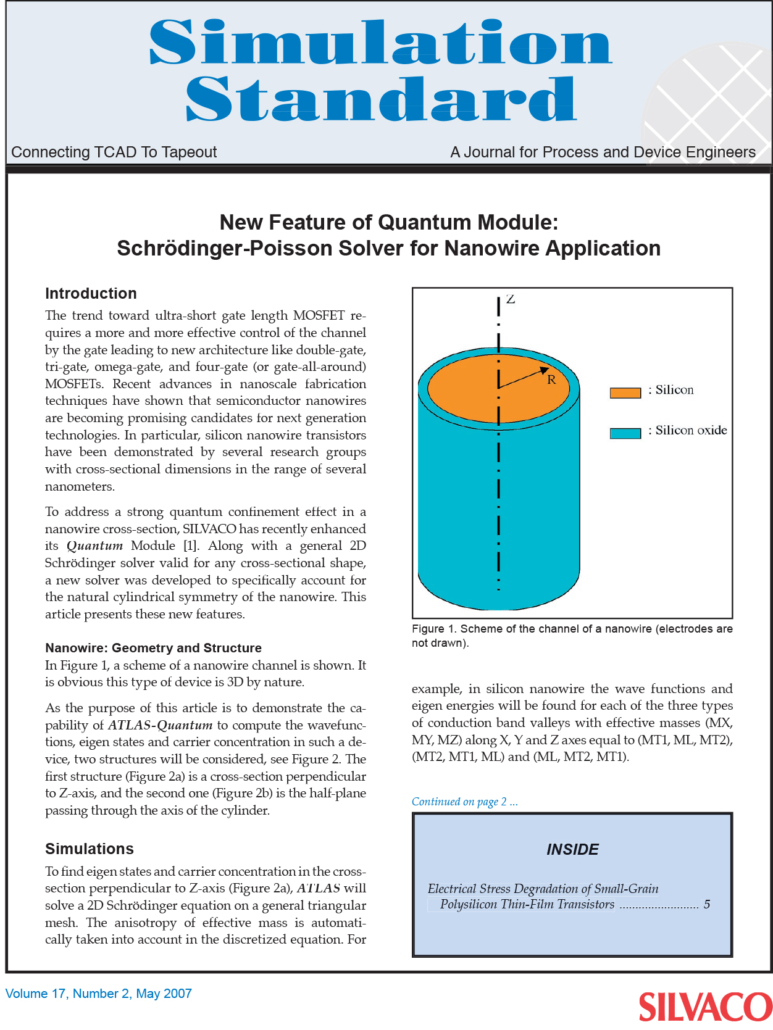
New Feature of Quantum Module: Schrödinger-Poisson Solver for Nanowire Application
Introduction
The trend toward ultra-short gate length MOSFET requires a more and more effective control of the channel by the gate leading to new architecture like double-gate, tri-gate, omega-gate, and four-gate (or gate-all-around) MOSFETs. Recent advances in nanoscale fabrication techniques have shown that semiconductor nanowires are becoming promising candidates for next generation technologies. In particular, silicon nanowire transistors have been demonstrated by several research groups with cross-sectional dimensions in the range of several nanometers.

