Simulation Standard
Technical Journal
A Journal for Process and Device Engineers
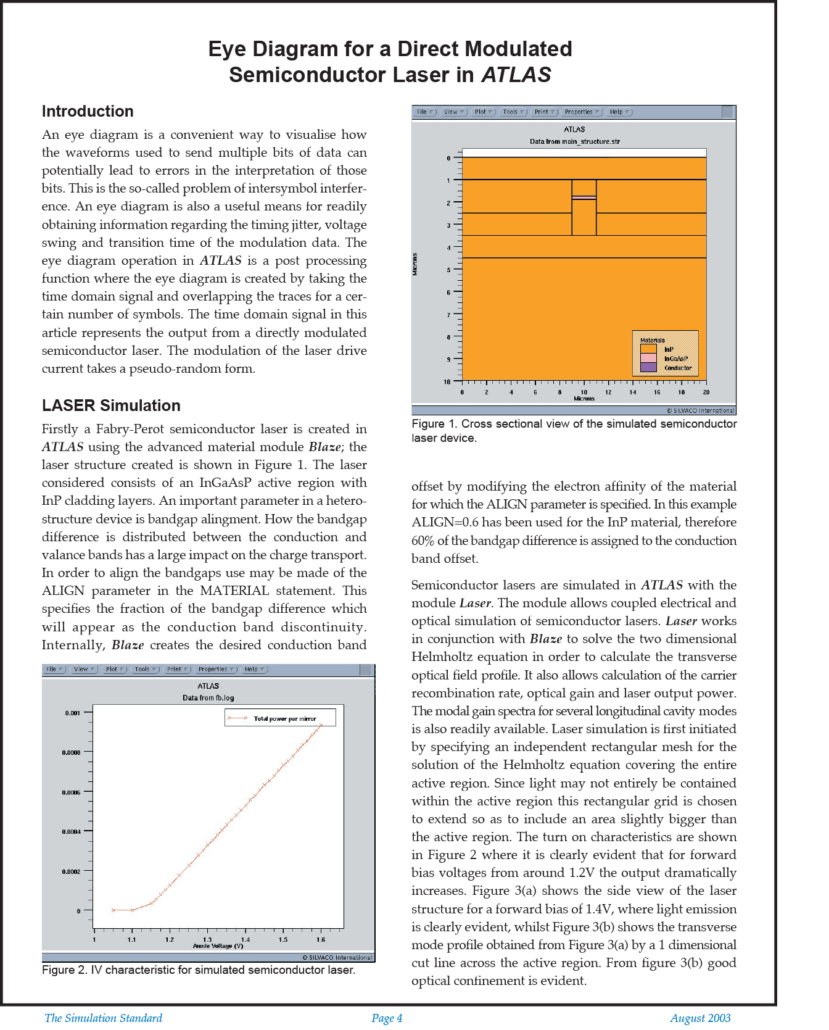
Eye Diagram for a Direct Modulated Semiconductor Laser in ATLAS
An eye diagram is a convenient way to visualise how the waveforms used to send multiple bits of data can potentially lead to errors in the interpretation of those bits. This is the so-called problem of intersymbol interference. An eye diagram is also a useful means for readily obtaining information regarding the timing jitter, voltage swing and transition time of the modulation data. The eye diagram operation in ATLAS is a post processing function where the eye diagram is created by taking the time domain signal and overlapping the traces for a certain number of symbols. The time domain signal in this article represents the output from a directly modulated semiconductor laser. The modulation of the laser drive current takes a pseudo-random form.
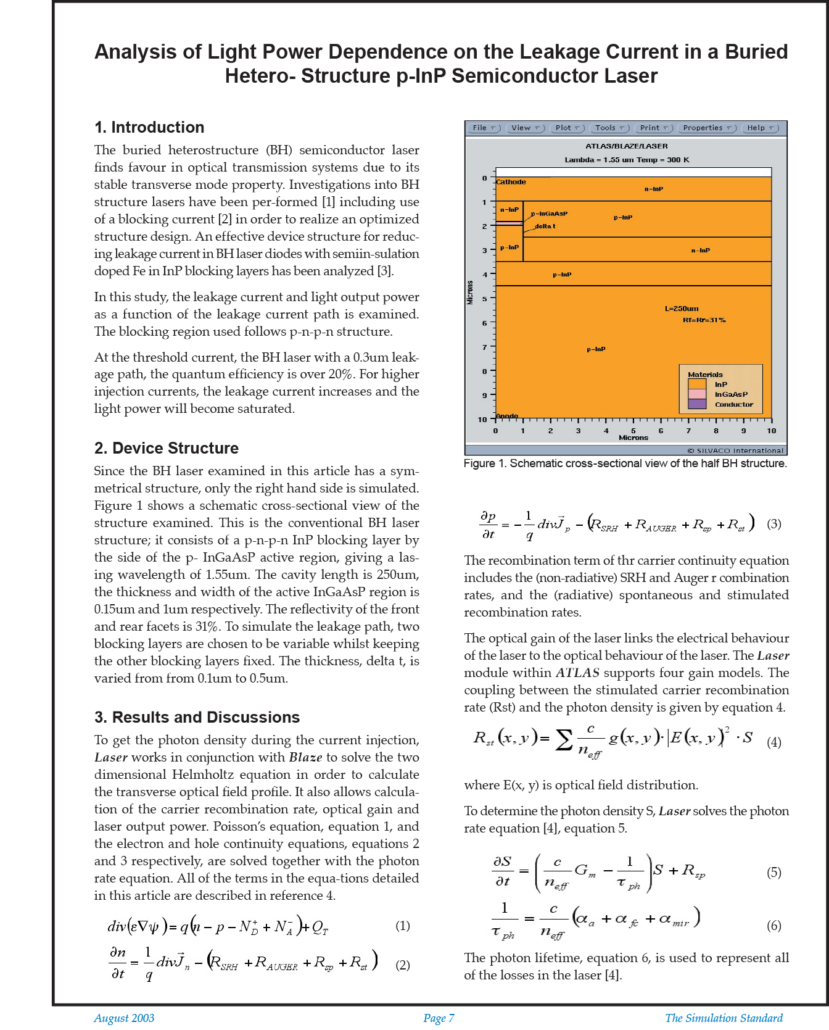
Analysis of Light Power Dependence on the Leakage Current in a Buried Hetero- Structure p-InP Semiconductor Laser
An effective device structure for reducing leakage current in BH laser diodes with semiin-sulation doped Fe in InP blocking layers has been analyzed [3]. In this study, the leakage current and light output power as a function of the leakage current path is examined. The blocking region used follows p-n-p-n structure.
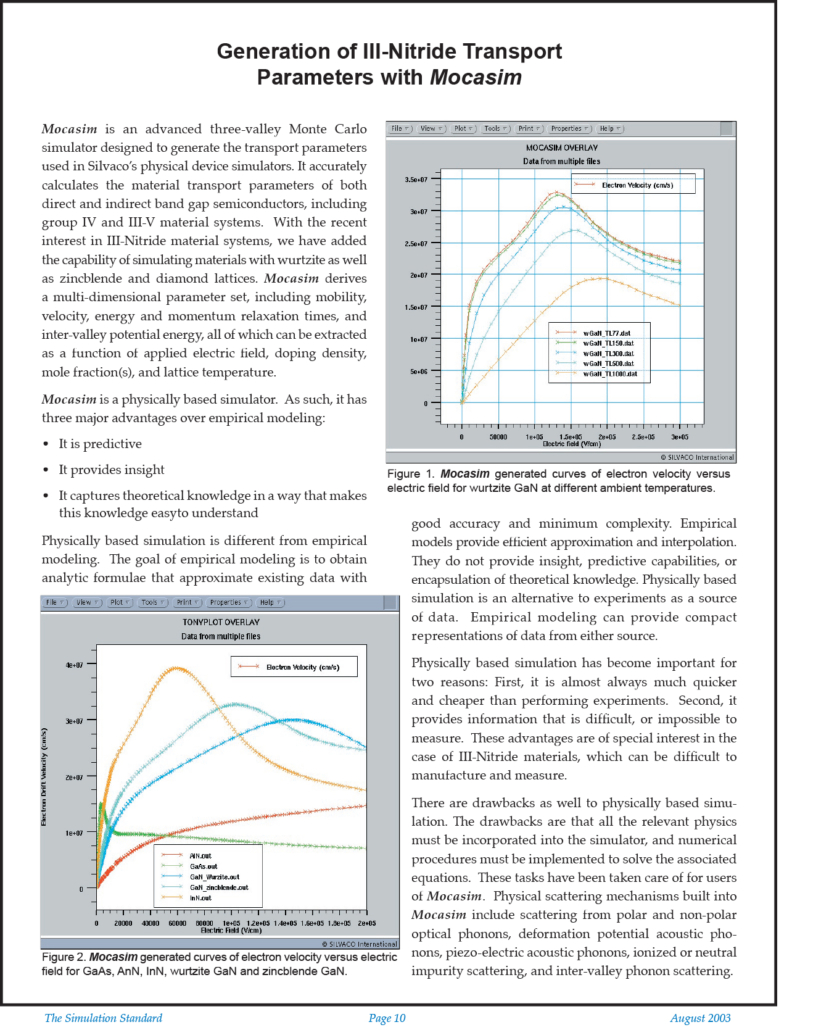
Generation of III-Nitride Transport Parameters with Mocasim
Mocasim is an advanced three-valley Monte Carlo simulator designed to generate the transport parameters used in Silvaco’s physical device simulators. It accurately calculates the material transport parameters of both direct and indirect band gap semiconductors, including group IV and III-V material systems. With the recent interest in III-Nitride material systems, we have added the capability of simulating materials with wurtzite as well as zincblende and diamond lattices. Mocasim derives a multi-dimensional parameter set, including mobility, velocity, energy and momentum relaxation times, and inter-valley potential energy, all of which can be extracted as a function of applied electric field, doping density, mole fraction(s), and lattice temperature.
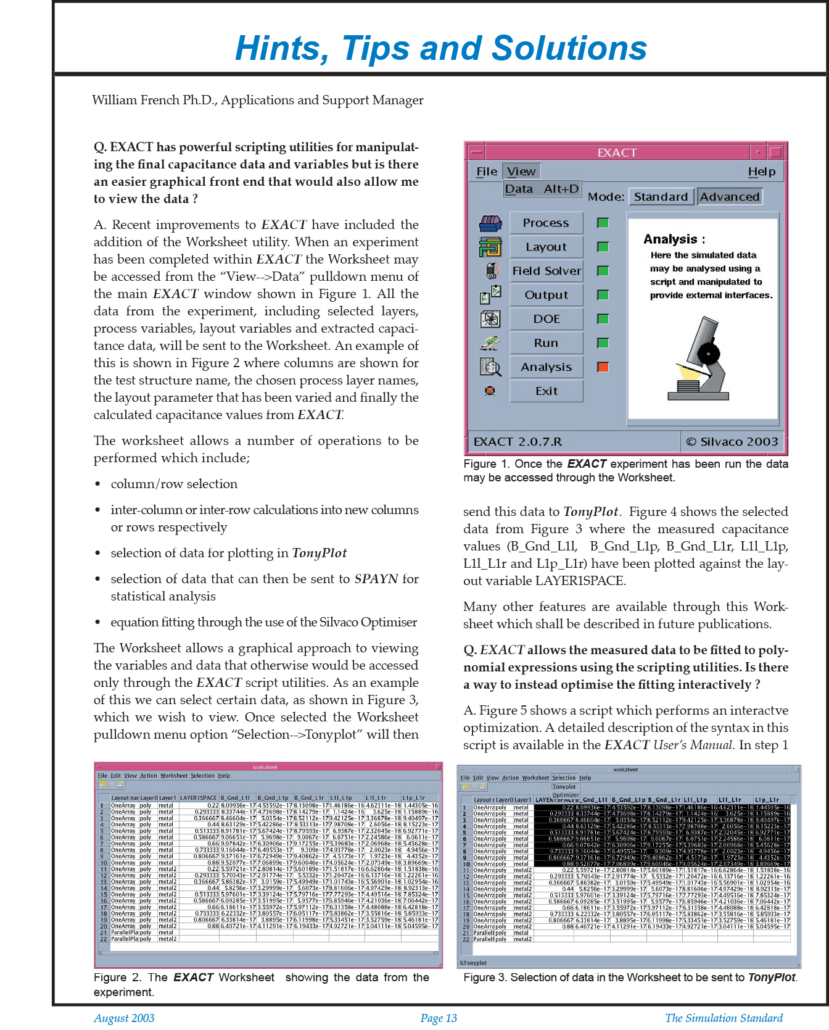
EXACT Worksheet Utility to View Variables and Data
Q: EXACT has powerful scripting utilities for manipulating the final capacitance data and variables but is there an easier graphical front end that would also allow me to view the data?

HiSIM V1.2 Model Parameter Extraction with UTMOST-III
HiSIM (Hiroshima university STARC IGFET Model) is one of the surface potential based Spice models [1], [2] and pioneered the iterative approach to obtain the surface potential applicable in compact models. The model aims for MOSFET technology of 100 nm or below. The parameter extraction procedure was introduced first by the model developers: Semiconductor Technology Academic Research Center (STARC) [3], [4]. Silvaco UTMOST-III introduced the first version of the local optimization strategies for HiSIM-1.1 in 2002 [5]. Since then, the parameter extraction methodology has been reviewed thoroughly. This article is meant to provide significant aspects on the HiSIM version 1.2 parameter extraction for UTMOST-III users.
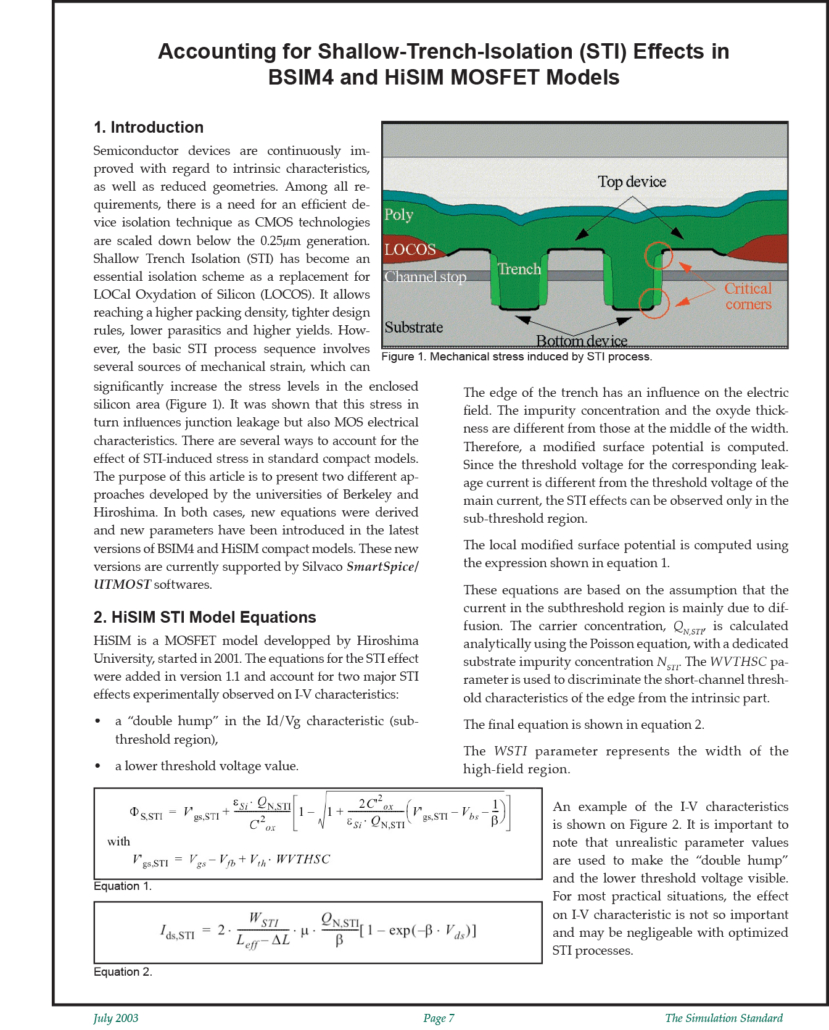
Shallow-Trench-Isolation (STI) Effects in BSIM4 and HiSIM MOSFET Models in SmartSpice & UTMOST-III
There are several ways to account for the effect of STI-induced stress in standard compact models. The purpose of this article is to present two different approaches developed by the universities of Berkeley and Hiroshima. In both cases, new equations were derived and new parameters have been introduced in the latest versions of BSIM4 and HiSIM compact models. These new versions are currently supported by Silvaco SmartSpice/UTMOST softwares.

