Simulation Standard
Technical Journal
A Journal for Process and Device Engineers
Simulation of Vertical Double-Gate SOI MOSFETs Using Device3D
This article will present the simulation methodology of a self-aligned double-gate MOSFET structure (FinFET) using SILVACO 3-D simulation suite. The double-gate MOSFET is one of the most attractive alternative to classical MOSFET structure for gate length down to 20nm. The main advantage of the FinFET is the ability to drastically reduce the short channel effect. In spite of his double-gate structure, the FinFET is closed to its root, the conventional MOSFET in layout and fabrication. 3-D numerical simulations of the FinFET are performed in this article, in order to validate the basic principles and to uncover several important aspects: evaluation of the length , width and quantum effects.

Non-Stationary Transport Effects: Impact on Performances of Realistic 50nm MOSFET Technology
We analyze quantitatively the real impact of technology on the needed level for carrier transport modeling. The results, based on theoretical analyzes, are applied to existing devices. This work shows which recipes must be used to evaluate the performances of advanced device architectures (down to 50nm gate length). An original point of this work is the investigation of technology influence (channel doping and LDD doping) on injection velocity at source side and on drain current. The results open the perspective of specific engineering of access regions in order to take full advantage of non-stationary effects on the drain current.

ATLAS can be used to perform large signal sinusoidal analysis
The Atlas syntax is flexible enough to allow the definition of sinusoidal nodal voltages by defining them on the SOLVE statement line. To illustrate this the structure shown in Figure 1 has been used. Before the sinusoidal pulse is applied a dc operating condition is set with
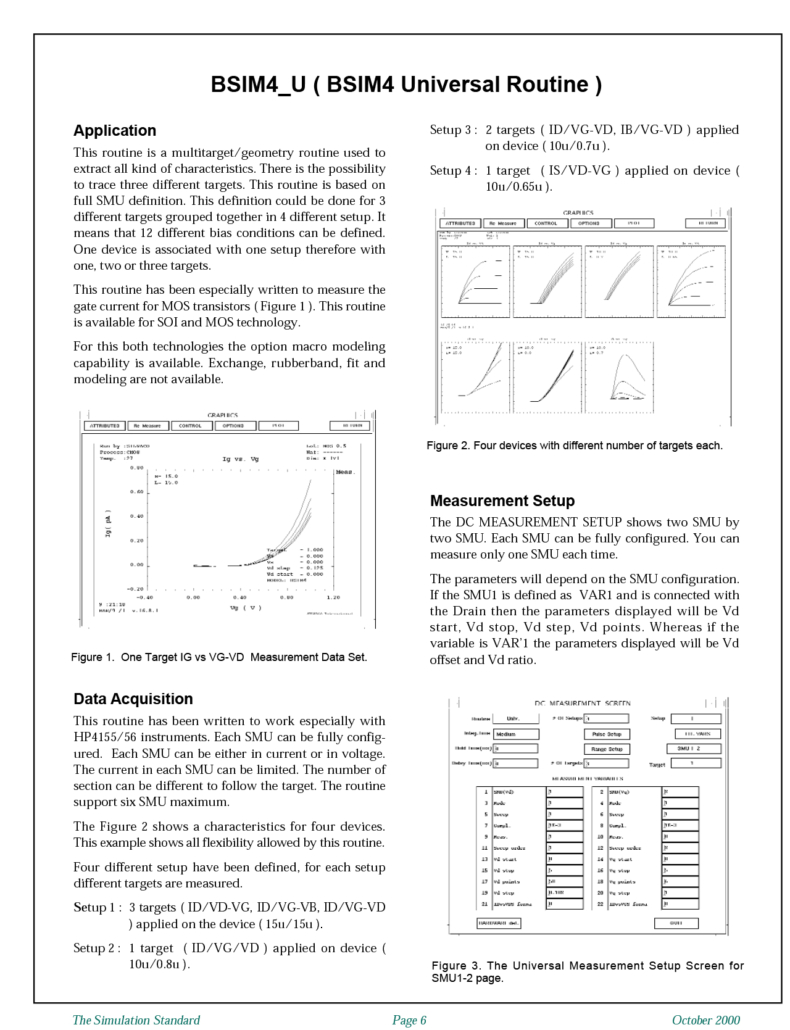
RF CMOS Modeling Using UTMOST III AC (S-Parameter) Module
This article presents a high frequency SPICE model parameter extraction method for CMOS devices. Current compact MOS models are developed for low frequency applications and provide good fits for DC, conductances and intrinsic capacitances. However for the gigahertz frequency range external components have to be modeled and added to the compact model as macro model elements. The macro model presented in this article provides good results up to 10 GHz.
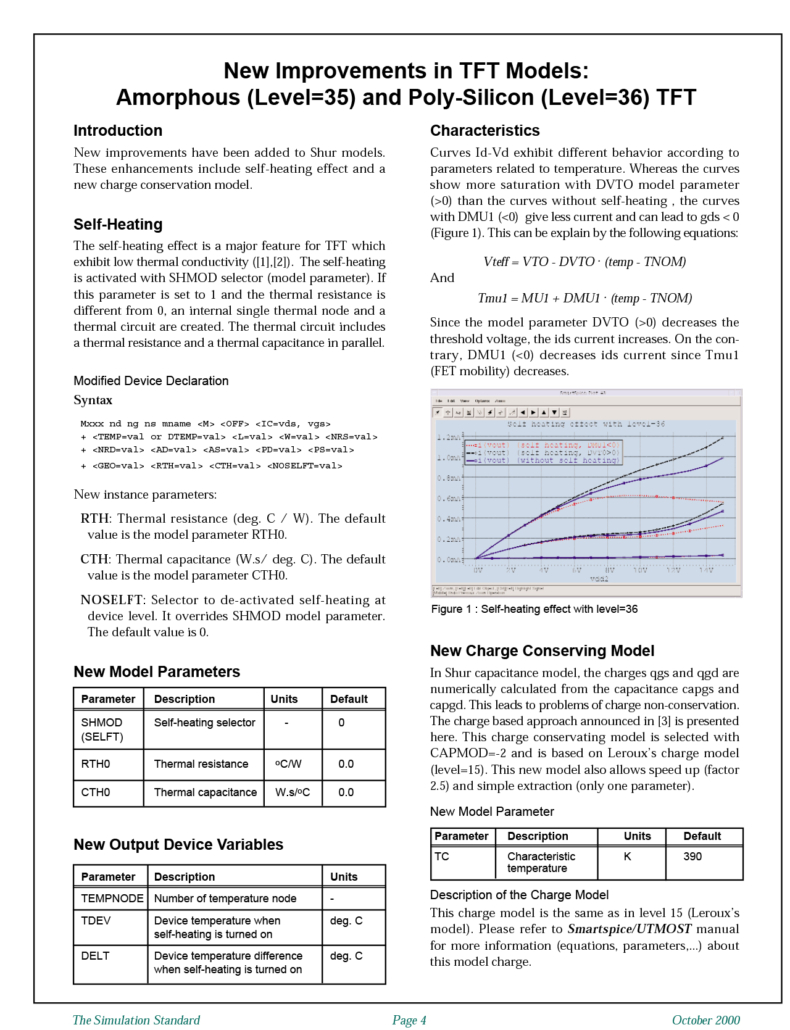
New Improvements in TFT Models: Amorphous (Level=35) and Poly-Silicon (Level=36) TFT
New improvements have been added to Shur a-Si:H and Poly-Si Thin Film Transistors models. These enhancements include self-heating effect and a new charge conservation model.

BSIM4_U ( BSIM4 Universal Routine )
This routine is a multitarget/geometry routine used to extract all kind of characteristics. There is the possibility to trace three different targets. This routine is based on full SMU definition. This definition could be done for 3 different targets grouped together in 4 different setup. It means that 12 different bias conditions can be defined. One device is associated with one setup therefore with one, two or three targets.ApplicationThis routine is a multitarget/geometry routine used to extract all kind of characteristics. There is the possibility to trace three different targets. This routine is based on full SMU definition. This definition could be done for 3 different targets grouped together in 4 different setup. It means that 12 different bias conditions can be defined. One device is associated with one setup therefore with one, two or three targets.

