Simulation Standard Technical Journal
A Journal for Process and Device Engineers
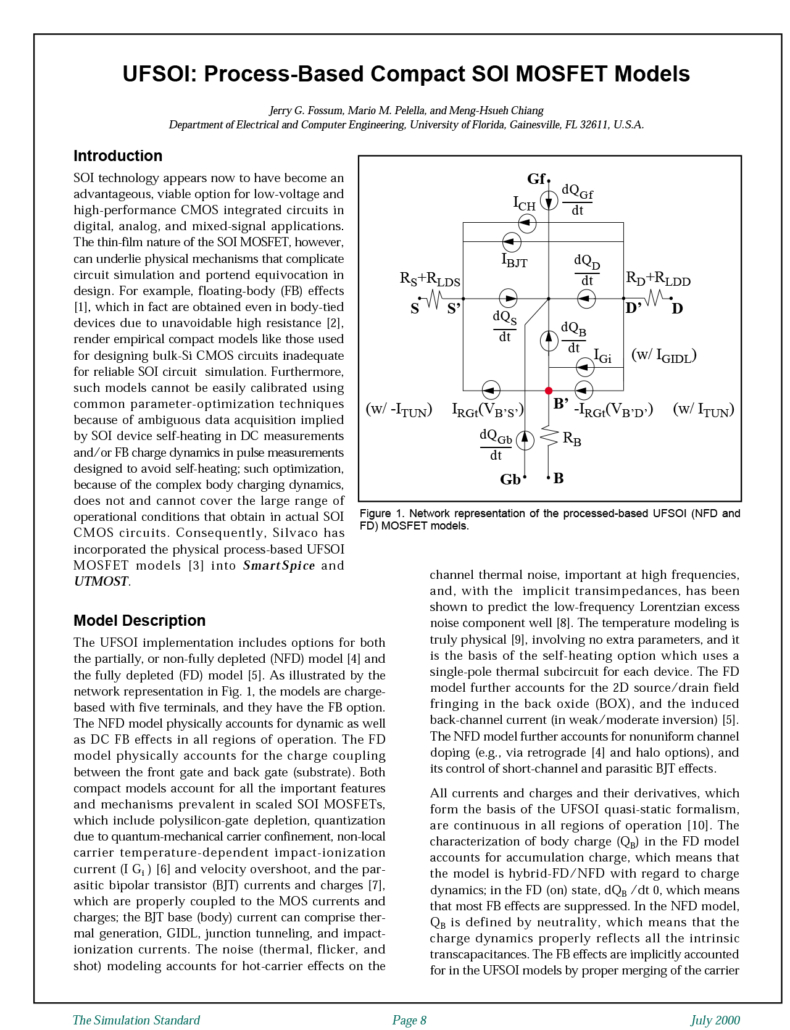
UFSOI: Process-Based Compact SOI MOSFET Models
SOI technology appears now to have become an advantageous, viable option for low-voltage and high-performance CMOS integrated circuits in digital, analog, and mixed-signal applications. The thin-film nature of the SOI MOSFET, however, can underlie physical mechanisms that complicate circuit simulation and portend equivocation in design. Consequently, Silvaco has incorporated the physical process-based UFSOI MOSFET models into SmartSpice and Utmost.

Hints, Tips, and Solutions June 2000
Q: To simplify netlist extraction, I specify one kind of diffusion resistors in my layout by means of a special resistor definition layer. To my surprise, the extracted value for one such resistor always exactly twice the value I expected, no matter how I stretch this resistor.
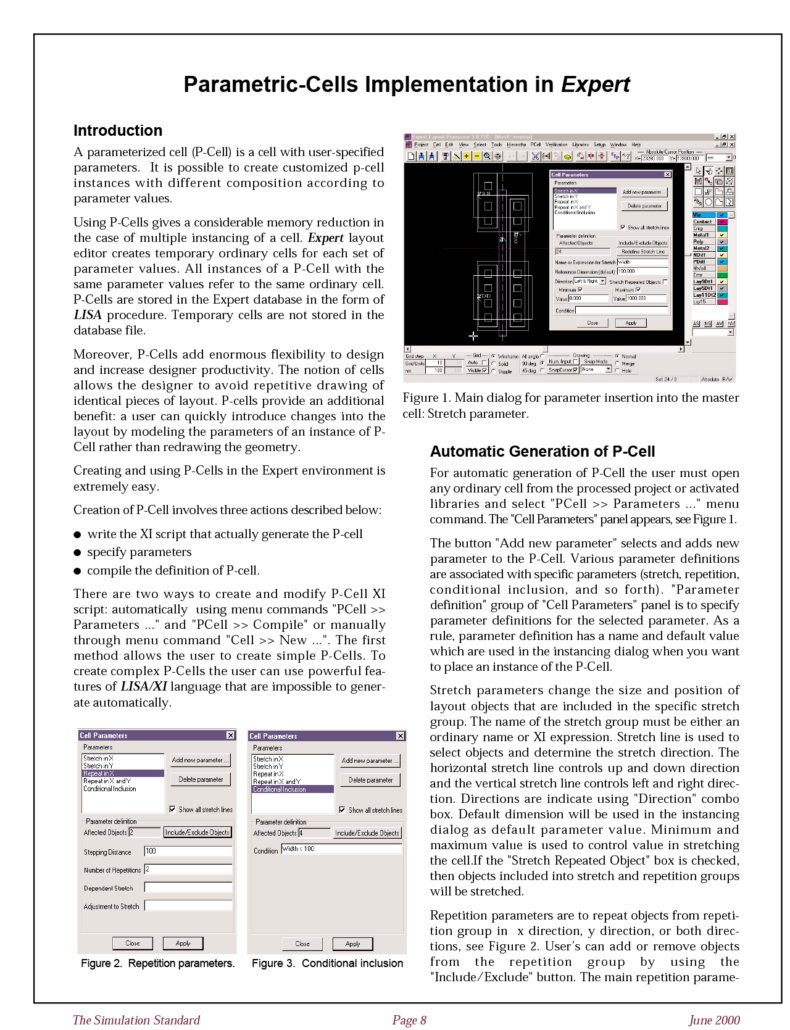
Parametric-Cells Implementation in Expert
A parameterized cell (P-Cell) is a cell with user-specified parameters. It is possible to create customized p-cell instances with different composition according to parameter values. Using P-Cells gives a considerable memory reduction in the case of multiple instancing of a cell.
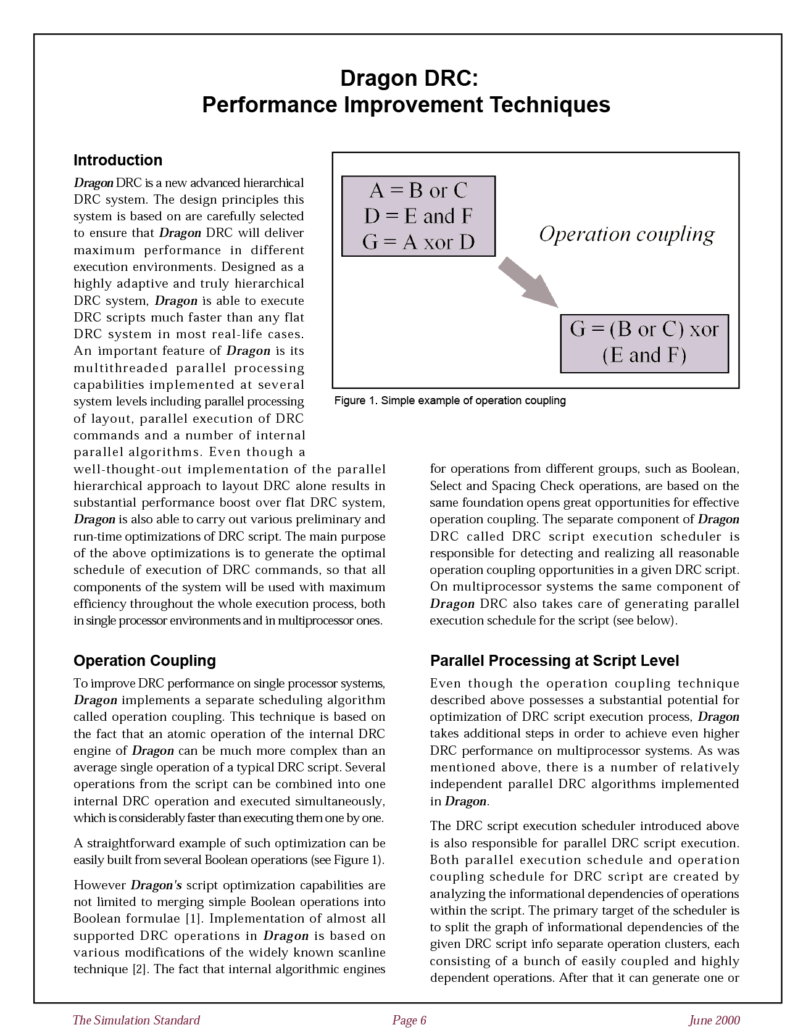
Dragon DRC: Performance Improvement Techniques
Dragon DRC is a new advanced hierarchical DRC system. The design principles this system is based on are carefully selected to ensure that Dragon DRC will deliver maximum performance in different execution environments. Designed as a highly adaptive and truly hierarchical DRC system, Dragon is able to execute DRC scripts much faster than any flat DRC system in most real-life cases.
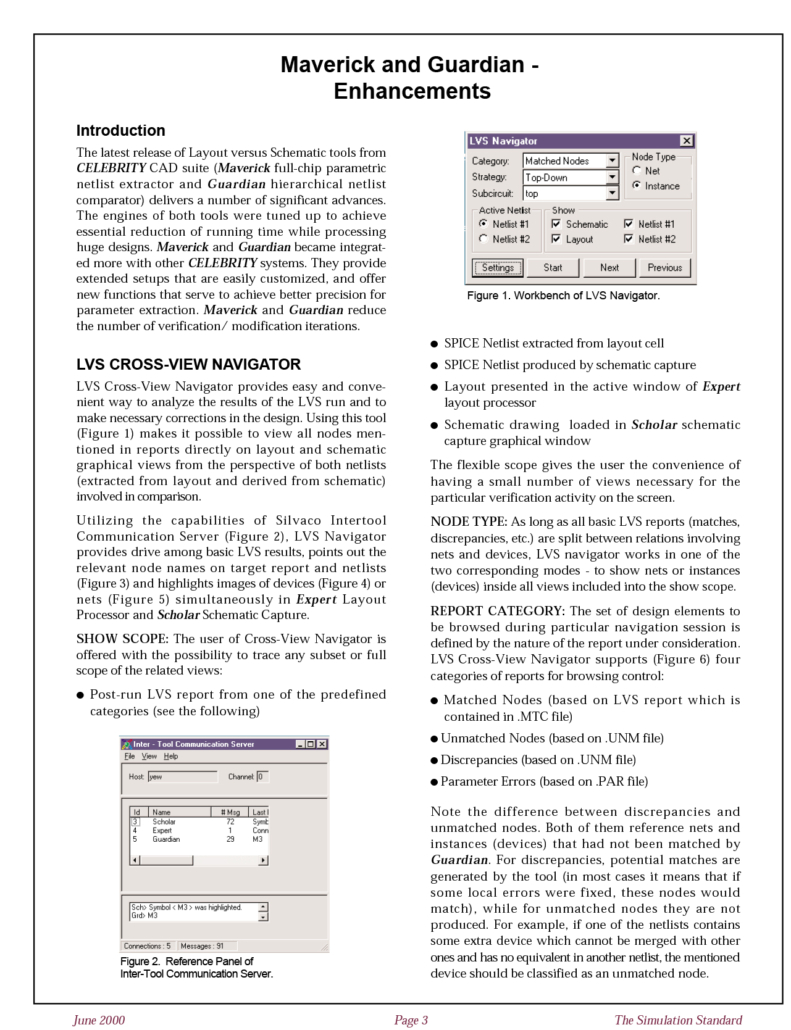
Maverick and Guardian – Enhancements
The latest release of Layout versus Schematic tools from CELEBRITY CAD suite (Maverick full-chip parametric netlist extractor and Guardian hierarchical netlist comparator) delivers a number of significant advances. The engines of both tools were tuned up to achieve essential reduction of running time while processing huge designs.

Design Version Control System for Expert
The DVCS subsystem of CELEBRITY CAD suite provides significant improvement in management of complex designs, design reuse and teamwork management. The most important features of DVCS are the means for version tracking and team design coordination.

