Modeling of Charge Distribution Using Schrodinger-Poisson Equations: Application to Double-Gate GAA-SOI Transistor
Introduction
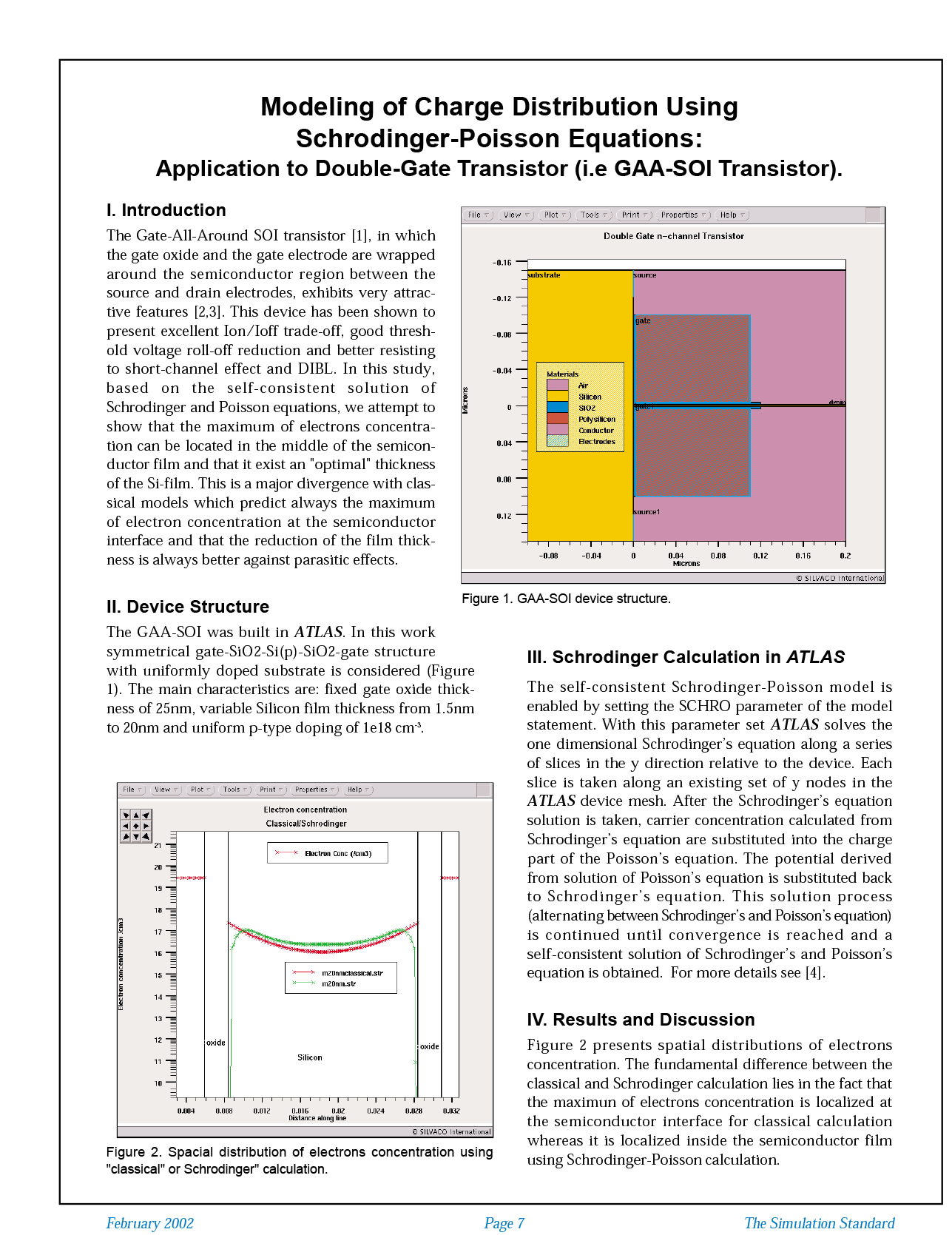
The Gate-All-Around SOI transistor [1], in which the gate oxide and the gate electrode are wrapped around the semiconductor region between the source and drain electrodes, exhibits very attractive features [2,3]. This device has been shown to present excellent Ion/Ioff trade-off, good threshold voltage roll-off reduction and better resisting to short-channel effect and DIBL. In this study, based on the self-consistent solution of Schrodinger and Poisson equations, we attempt to show that the maximum of electrons concentration can be located in the middle of the semiconductor film and that it exist an “optimal” thickness of the Si-film. This is a major divergence with classical models which predict always the maximum of electron concentration at the semiconductor interface and that the reduction of the film thickness is always better against parasitic effects.