Single and Dual Port SRAM Compilers
Compilers Overview
Silvaco has 25 years’ experience in compiled memory design. Its technology is silicon proven in thousands of designs and millions of wafers.
- Compilers for SRAM (single and dual Port), Register File (1 port and 2 port), and ROM
- Deployed at 12 different foundries and IDM’s
- Available in processes down to 22nm
SRAM Compiler Features
- Optimized for low power, general purpose and high performance applications
- Effective power management with multiple power modes and options
- High Performance through Multiple voltage threshold (Vt) options and operating modes
- High Yield
- Verified for global and local variation tolerant design
- ECC bits, word size and address flexibility for redundancy
- Available technologies include 180nm, 152nm, 130nm, 110nm, 90nm, 85nm, 65nm, 55nm, 40nm, 28nm and 22nm
- CMOS processes variants covered include G, LP, SOI, and SRAMs in CMOS in the High Voltage, BCD, and eFlash foundry offerings
- Can easily port to other nodes and processes
SRAM Architecture
- Designed primarily for low power operation
- High density option provides industry leading area and density
- Multiple low power modes for 55nm, 40nm and below include Nap, Retention, Nap+Retention modes
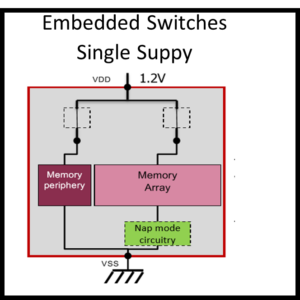
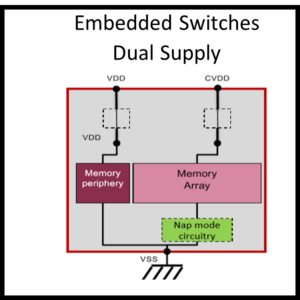
- Embedded switches support
- Available in
- Single supply
- Dual supply rail for periphery and core
- Configurable write mask option
- Optional support for Built in Self Test and Repair (BIST/R)
| Feature | Benefit |
| High density | Industry leading area |
| Partitioned array | Extended battery life |
| Several operating modes | Up to 50% lower power consumption |
| Data retention mode | Reduce leakage current |
| BIST (optional) | Increase reliability and yield |
SRAM Low Power Operation Modes
Silvaco SRAM compilers offer a range of low power operation modes with different leakage and wake-up times.
| Mode | Description | Leakage* |
| Active
Core: On @ Vdd |
· Read or write
· Core and Periphery powered and operational. · Dynamic power and small Leakage power consumption |
— |
| Standby
Core: On @ Vdd |
· No read or write.
· Core and Periphery powered but not operational · Small Leakage power but no Dynamic power consumption · Quick Wake Up time |
1.00 x |
| Nap*
Core: On @ Vdd |
· Source Biasing turned on
· Intermediate low power state · Low leakage power consumption · Quick Wake Up time (1 clock cycle), but a bit slower than Standby Wake Up time |
0.69 x |
| Retention*
Core: On @ < Vdd Periphery: OFF |
· Periphery power turned off
· Core at minimum voltage to retain data · Lower Leakage power consumption than Nap · Slow Wake Up time depends on powering up periphery switches and other circuits |
0.54 x |
| Retention + Nap*
Core: On @ Vdd |
· Source Biasing turned on
· Core maintained at nominal voltage · Lower Leakage power consumption than Retention · Slow Wake up time depends on powering up periphery switches and other circuits |
0.28 x |
| Shutdown (Data Content Lost)
Core: OFF |
· Core and Periphery switched off
· Lowest Leakage power consumption · Slowest Wake Up time |
— |
*Advanced power modes are available for 55nm, 40nm, and below nodes.
Memory Configurations
Silvaco SRAM compilers support different voltage supply configurations. The compilers also support a wide range of mux and word width configurations.
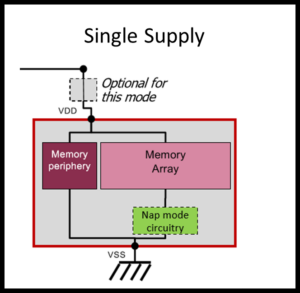
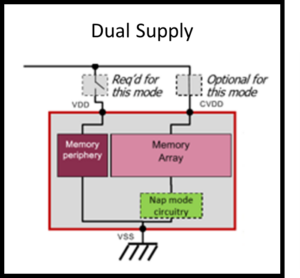
Silvaco SRAM compilers also support embedded switches for finer integrated control of low power operation.